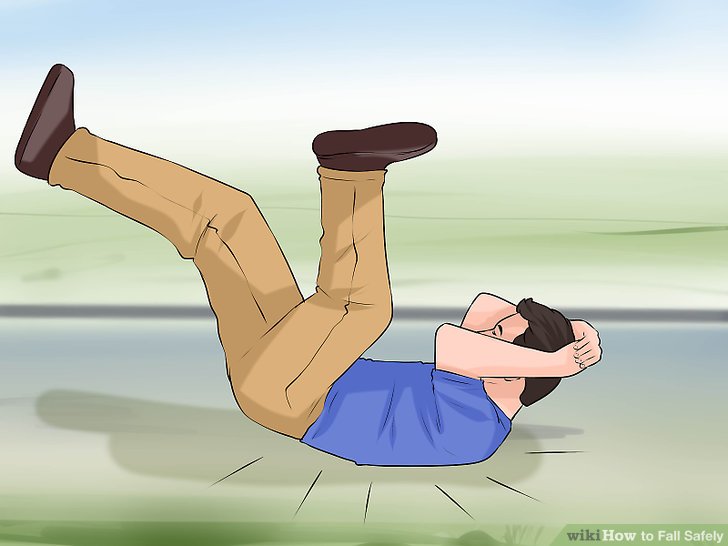
I have been teaching water fitness for 26 years. Clearly I enjoy exercising. But I know there are a lot of people out there who do not exercise. The excuses include not being motivated, not having enough time, being too tired, exercise is not fun, being too out of shape and not liking to sweat.
Motivation. Everyone wants to look younger and live longer. The secret to longer life is not a magic pill but exercise. Scientists can predict how long someone will live by how well they perform 5 simple tasks. How many times can you stand up from a chair and sit back down in 60 seconds? How long can you balance on one leg? How long is your stride length? How is your grip strength? How good is your posture? A good reason to exercise is to make improvements in these areas to improve your longevity and make the activities of everyday life easier.
Not Enough Time. Instead of trying to find time, try to make time. Some activity is better than none. Find a time during your day when you are free of commitments and schedule some exercise during that time. It doesn’t have to be a lot of time. Start with 10 minutes and increase it by a minute a week. Soon it will become part of your routine.
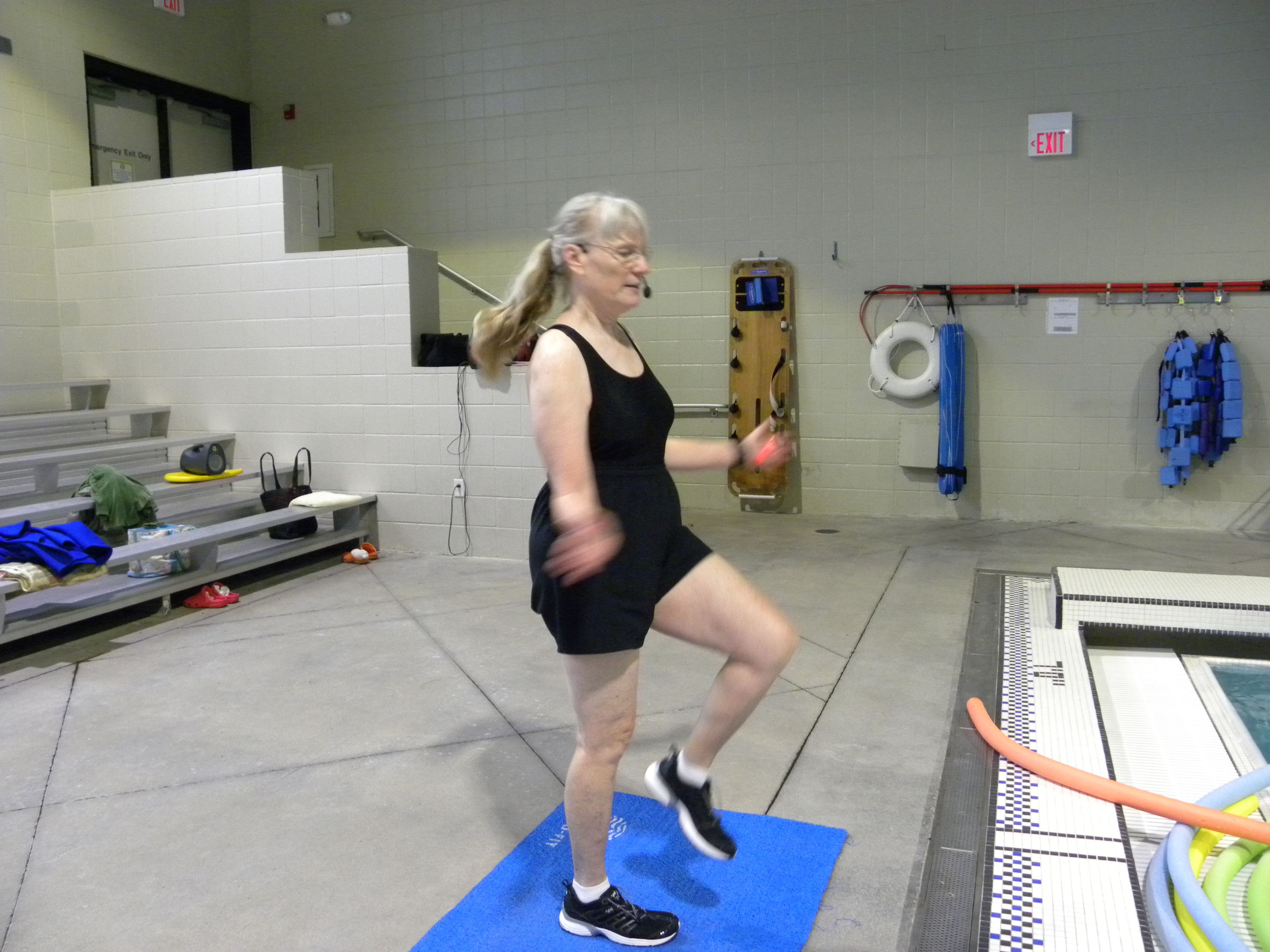
The remaining excuses. Once your fitness starts to improve, you will find you have increased energy. If one type of exercise is not fun, try something active that you do enjoy. Here’s where I put in a plug for water exercise. Hanging out in the pool when we were children was so much fun that many of us find getting in the water to exercise is really enjoyable. The buoyancy of the water supports your weight so that it seems easier to exercise even if you are out of shape. And the water cools your body so that you are not aware that you are sweating.
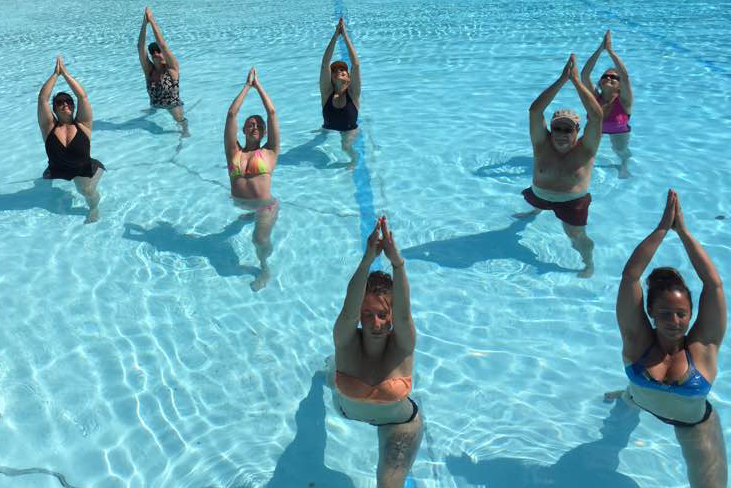






Many of the simple tasks that predict longevity can be worked on in the pool. Squats can improve your ability to stand up from a chair and sit back down. The pool is the perfect place to work on balance because the water supports the body and reduces the fear of falling while at the same time water movement makes balancing more challenging. You can work on increasing stride length by water walking. Hand grip exercisers are best for improving grip strength, but gripping pool equipment helps some. You can also concentrate on exercising with good posture in the water to help improve posture on land.
Exercising regularly makes the activities of daily life such as climbing stairs, playing with grandchildren and carrying groceries easier. It also improves blood flow to the brain which decreases the risk of cognitive decline. We cannot stop from aging, but we can work to maintain our functional fitness well into our retirement years.
See you in the pool!

Chris Alexander