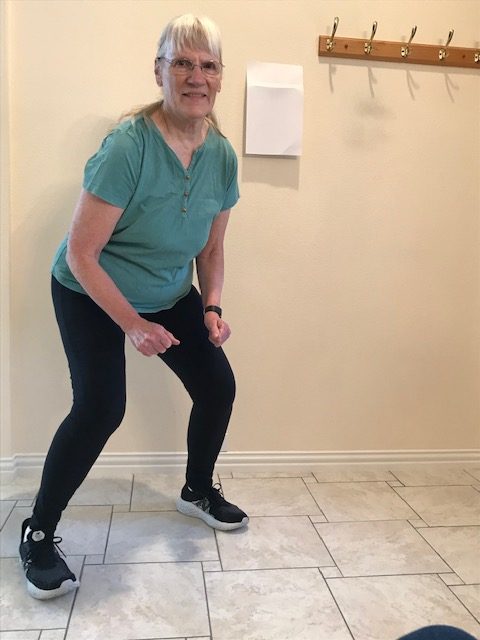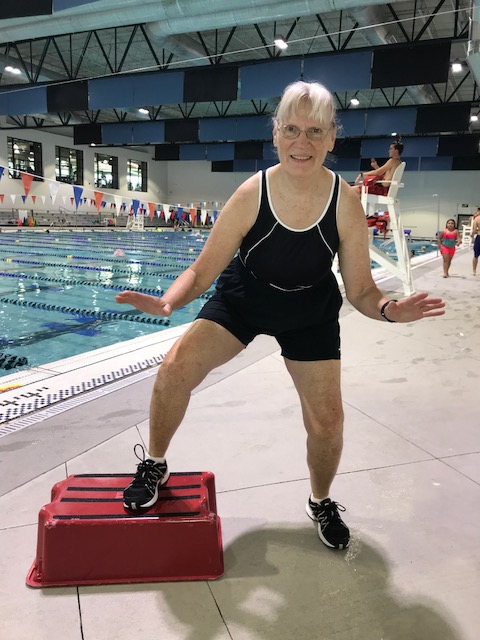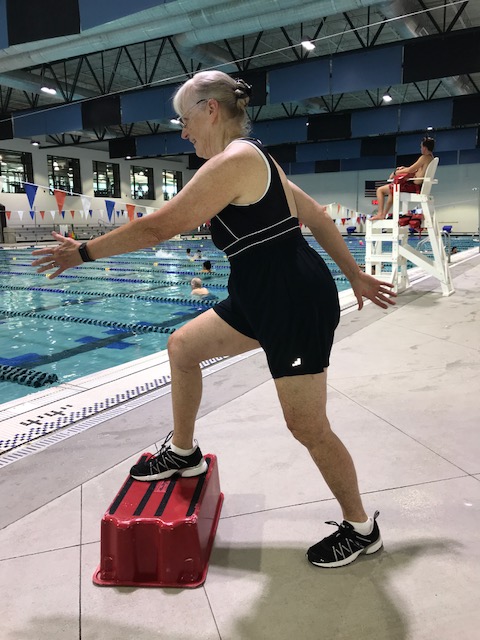The quick answer to the question is: strengthen the muscles that are used the least. Most of those muscles are on the back (posterior) side of our body because the movements we make are usually in front (anterior) where we can see what we are doing. The muscles of our joints are primarily organized in pairs. One muscle bends (flexes) the joint, its pair straightens (extends) the joint. The muscle in front usually does the flexion. The muscle in back usually does the extension. The exception is the knee joint, where the muscle in back does the flexion and the muscle in front does the extension. When one of the muscles contracts, its muscle pair is stretched. You can easily see that if we are contracting the muscles in front more often, then they become stronger than the muscles in back that get stretched more often. The main muscle pairs are:
- Anterior deltoid and posterior deltoid – front and back of the shoulder joint
- Biceps and triceps – front and back of the elbow joint
- Rectus abdominis (abs) and erector spinae – front and back of the lumbar spine (the erector spinae is not labeled in the picture above because it is underneath the other muscles of the back)
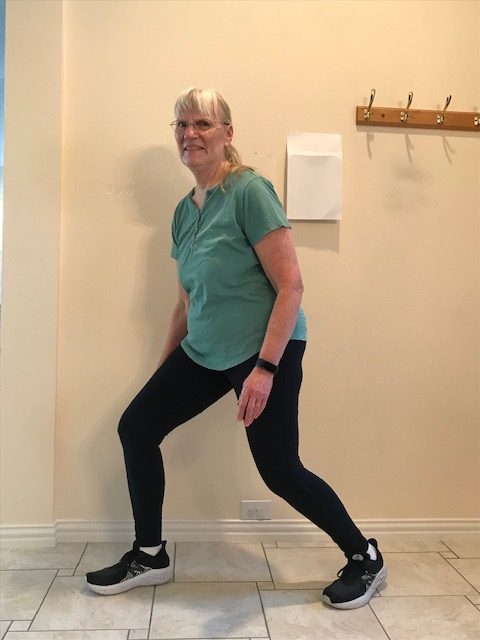
- Iliopsoas (hip flexors) and gluteus maximus – front and back of the hip joint (the iliopsoas is not labeled in the picture because it is a deep muscle on the front of the hip)
- Hip adductors (inner thigh) and abductors (outer thigh) – inside and outside of the hip joint (the adductors are not labeled)
- Quadriceps and hamstrings – front and back of the hip joint and the knee joint
- Tibialis anterior (shin) and gastrocnemius (calf) – front and back of the ankle joint
In a water fitness class we can exercise the posterior deltoid by doing a breaststroke or an arm swing with emphasis on swinging to the back. We can exercise the triceps by pressing the water down toward the floor. We can exercise the erector spinae by traveling backward. We can exercise the gluteus maximus with a skate kick (a straight leg kick to the back) and with cross-country ski emphasizing the backward motion. We can exercise the abductors with wide leg jog, kicks side to side and jumping jacks, emphasizing the motion out to the side. We can exercise the hamstrings with heel jog (hamstring curls) and skateboard. The tibialis anterior is weaker than the gastrocnemius; we exercise the shins in the pool when we do knee lifts or jog with the feet flexed because we are lifting water with the top of the foot every time we lift the knee.
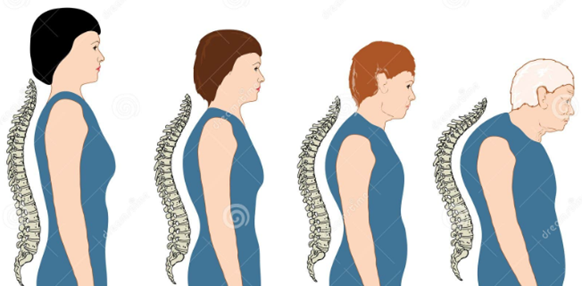
Another muscle group that needs strengthening is the trapezius, rhomboids and latissimus dorsi (lats). The rhomboids are not shown because they are in the center of the upper back beneath the trapezius. These muscles are important for posture. As we age, we tend to get rounded shoulders and our head falls forward. We can avoid some of this by keeping those postural muscles strong. Exercise the trapezius and rhomboids with a shoulder blade squeeze, upright row and crawl stroke. Exercise the latissimus dorsi with a lat pull-down (jumping jacks arms) emphasizing the downward motion and by touching the palms (or finger tips) behind the back.
Although it is typical to exercise all the muscles in an aquatic strength training class, it is a good idea to sometimes focus more on the muscles that need strengthening. Afterwards you may want to stretch the stronger muscles which tend to be tighter since they don’t get stretched as much, particularly the hip flexors, inner thigh, quadriceps and calf muscles.
It is very difficult to find a good clip art picture that clearly shows all the muscles. If you are interested in learning more about the muscles, go to pages 25-36 in the AEA Aquatic Fitness Professional Manual, or find a good anatomy book. There is more information about aquatic strength training, including lesson plans, in my book Water Fitness Progressions.
See you in the pool!